What is a solar eclipse?
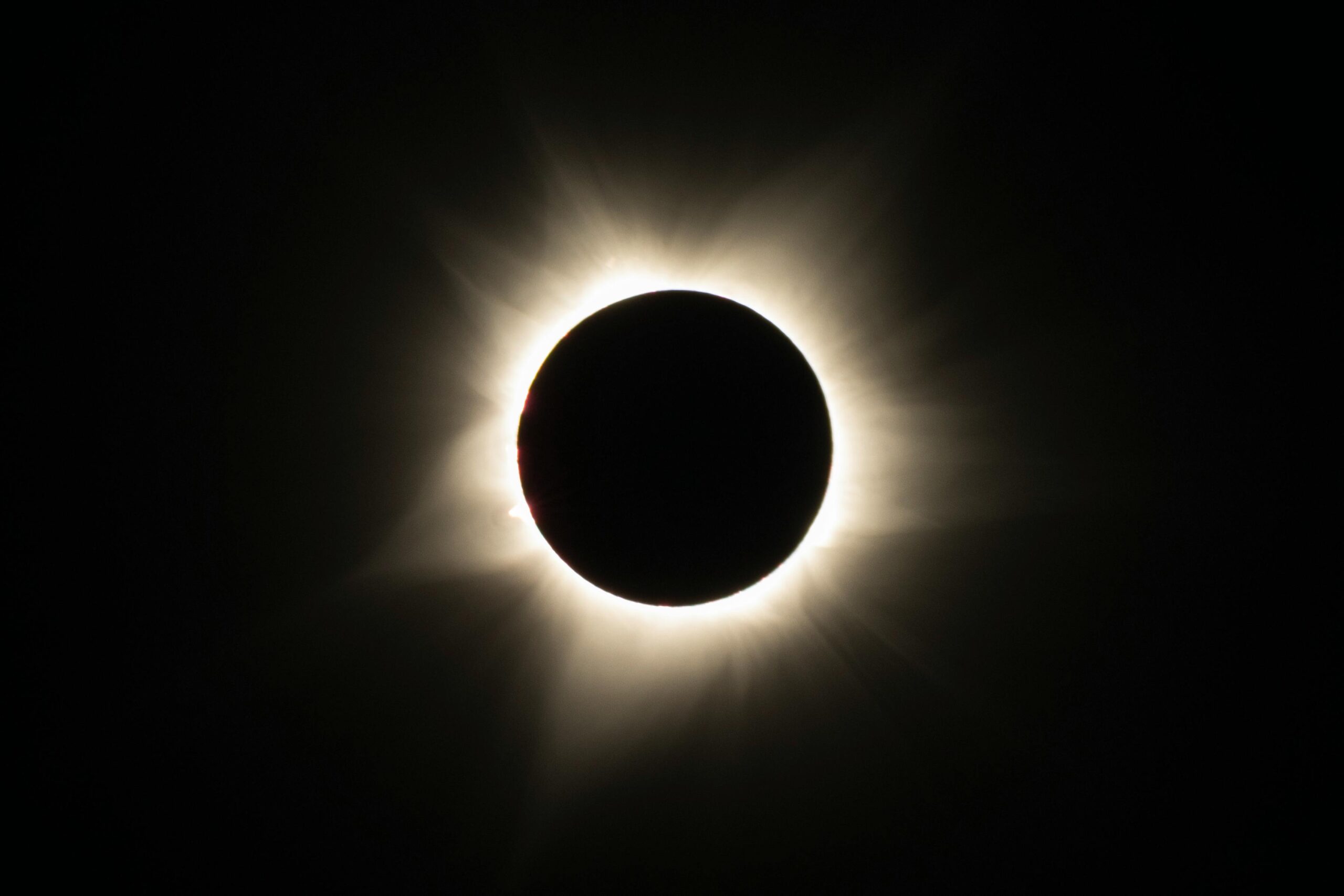
A solar eclipse occurs when the moon passes between the sun and the Earth, casting a partial or entire shadow on the planet. Total eclipses are rare because they required a closer alignment of the sun’s and moon’s centers. This natural occurrence occurs every six months during the eclipse season because of axial parallelism in its orbit. Solar eclipses, both ancient and modern, were believed to be caused by supernatural forces or ominous omens. Chinese scientists only began studying eclipses in the fourth century; however, we can now forecast them with remarkable accuracy thanks to the discovery of the Saros Series. For thousands of years, the period of 223 lunar months has been utilized to forecast eclipses for thousands of years.
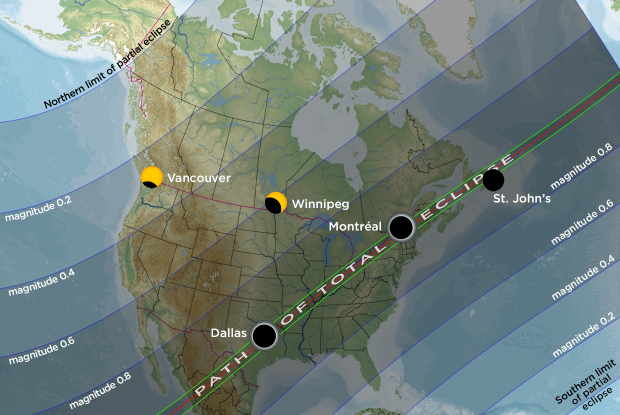
The trajectory
The total solar eclipse will be visible throughout North America, from Torreón, Mexico, to Newfoundland and Labrador. Major cities such as Austin, Texas, New York City, Montreal, Toronto, and Delaware will be able to experience the stunning sights provided by the total solar eclipse. For example, on Monday, April 8, 2024, Montreal will have 1.25 minutes of absolute darkness. The eclipse begins at 2 p.m. and ends at 4:36. In fact, the last time Montrealer experienced a total eclipse was in 1932, and it was a once-in-a-lifetime event because no other total solar eclipses are expected in the following 180 years.
Why are eclipses potentially dangerous?
The answer is simple. During a partial eclipse, the eyes become more vulnerable to UV radiation from the sun, which can enter the retinal tissues and burn the retina. These damaging rays can enter more easily because the pupil dilates in darker situations, which occurs when you wear polarized sunglasses. It can cause the burning of important cells called macula, which are responsible for our fundamentally clear vision. Polarized sunglasses and lenses are the only way to appreciate the beauty of a partial eclipse. When it comes to total eclipses, you can only remove your glasses during totality because the moon has covered the sun, reducing the intensity and amount of UV radiation.
